A key performance indicator (KPI) is a quantifiable metric that reflects the performance of a business in achieving its overall goals and objectives.

KPIs link various levels of an organization with clearly defined targets and benchmarks. They define a few measurements, usually less than twenty, that are key to the success or failure of an organization.
Balanced Scorecards
One tool used to summarize key performance indicators is a scorecard. In order to prevent a reliance on strictly financial measures, the balanced scorecard was developed in 1992 by Robert Kaplan and David Norton. It measures the goals in each of the strategic areas of an organization, including the following perspectives:
- Customer: meeting customer requirements and satisfaction objectives
- Operations: performance of critical internal processes
- Financial: typical financial measures such as revenue, profitability, productivity
- Learning and growth: innovation, technology, sustainability

Scorecards help to translate the strategic vision into operational terms, communicate the critical areas to the rest of the organization, and link it to functional objectives. Four to seven relevant scorecard measures are developed for each strategic goal in the organization’s strategic plan, in each of the four perspectives, as well as the expected outcomes for each goal.
Example of a Balanced Scorecard
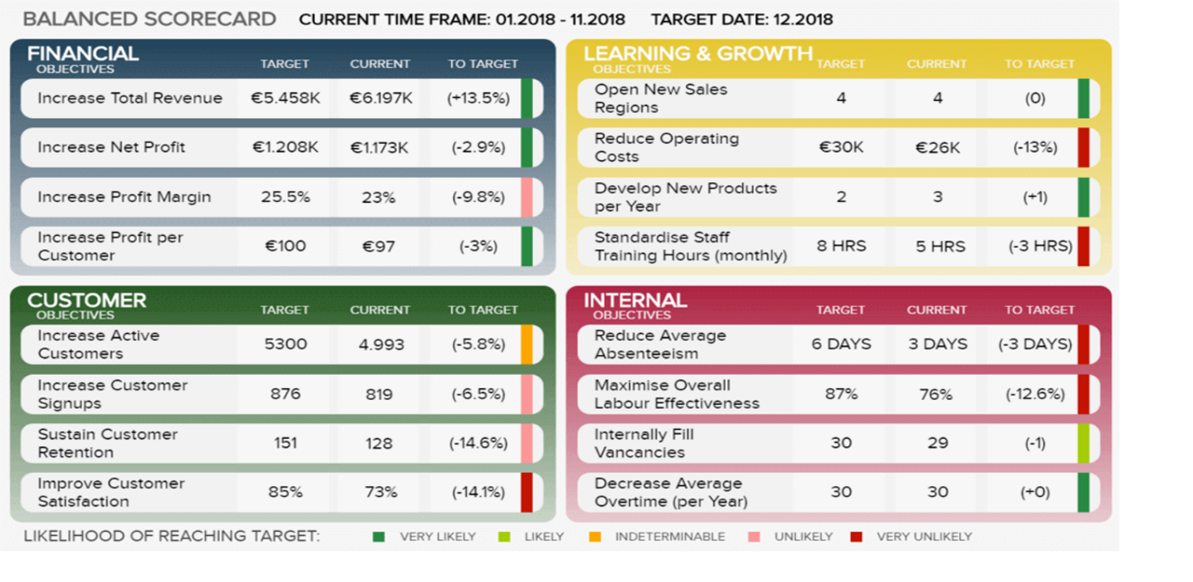
Web-based scorecards are often referred to as dashboards, which are “an easy-to-read management tool similar to an automobile’s dashboard designed to address a wide range of business objectives by combining business intelligence and data integration infrastructure, enable companies to retrieve data from their enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, see real-time status and progress, and make the information widely accessible, based on the security of the dashboard” (APICS Dictionary, 16th edition).
