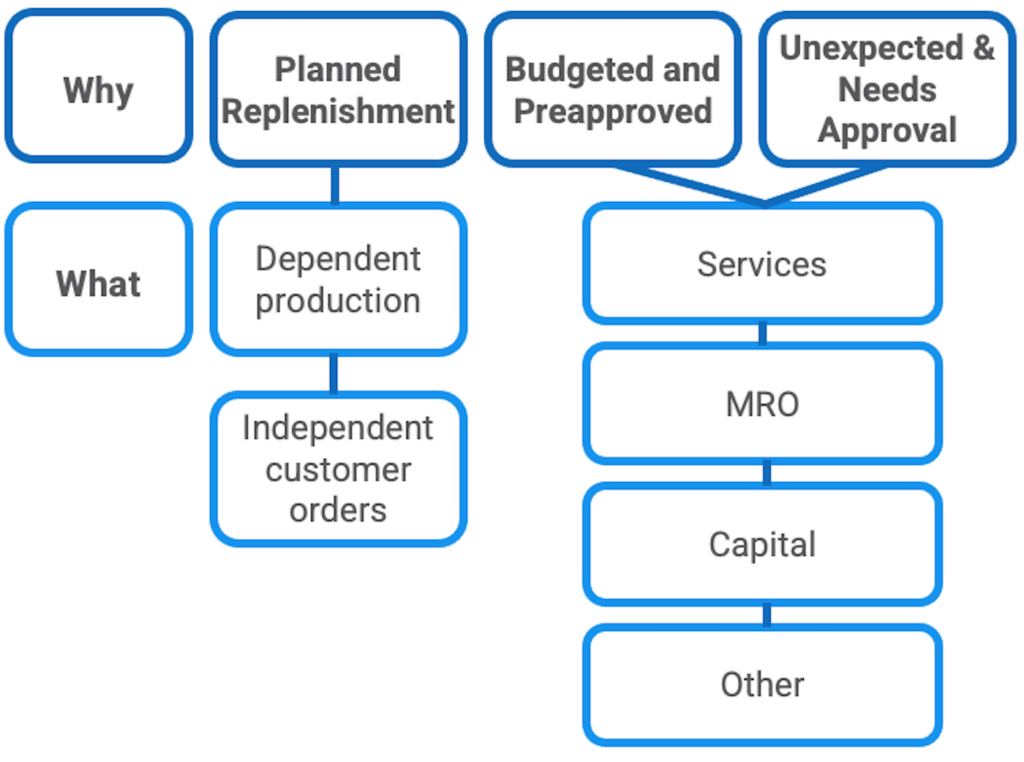
There are three types of requisitions: planned, budgeted and pre-approved, and unexpected requiring approval. Company policies guide the requisition process, specifying pre-approved goods and services, who can generate requisitions, and the monetary value that must be approved before processing.
Requisitions can come from various sources, including maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) orders or services with a requisition process. MRO orders begin as a requisition and move through sourcing, pricing, and authorization stages. Planning for capital equipment requisitions requires a detailed process that involves thorough analysis, including assessing the return on investment. However, this course mainly focuses on requisitioning raw materials (and subassemblies), MRO goods, and planned replenishment in a production or manufacturing setting.
Planned Replenishment
When operating in a manufacturing setting, the need for raw materials or subassemblies is typically generated by material requirements planning (MRP) systems or kanban. These systems then create requirements for production and distribution inventories. To manage planned replenishment for independent demand, order point or periodic review order techniques are employed.
To initiate planned replenishment, the purchase order management process requires the maintenance of key database elements. These include the item master, supplier master record, and price master. Additionally, variable database files such as open requisitions, open purchase orders, and purchasing history must be kept current and accurate. It is crucial that these files are maintained at 100% accuracy at all times.