When a company needs to buy certain materials, they use purchase requisitions to request authorization from the purchasing department. These internal documents specify the needed quantities and a specific time frame. Once the purchasing department approves the requisition, a purchase order is typically created. Different materials, services, and capital equipment may require different methods for generating purchase requisitions.
In the context of material requirements planning (MRP), raw materials and semi-finished goods will be turned into planned orders, which will then be evaluated by the planner or planner/buyer. Depending on the company’s policies, this step may be the only requirement before the materials are ordered.
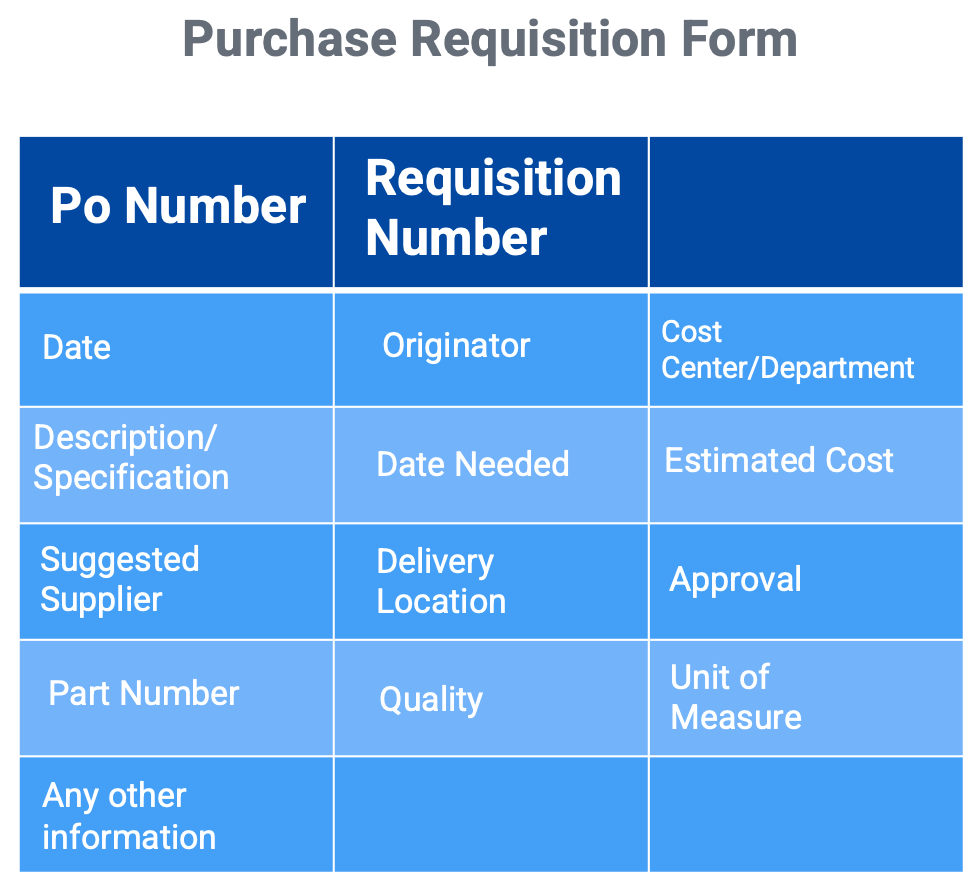
If materials, services, or capital equipment are not included in the MRP plan, the user or department responsible must generate a requisition. This can be done either through a manual paper-based system or an electronic process. The image provides an example of the necessary information required for the requisition.
To ensure a smooth requisition process, it is necessary to have a company policy in place that outlines the required approval levels. Certain materials, MRO items, and services below a certain threshold can be purchased using a P-Card, which is a company charge card that allows for procurement of goods and services without a purchase order. However, it is important to adhere to policies and procedures in these instances to prevent maverick spending and avoid unnecessary steps in the purchasing cycle. Depending on the complexity, time, and value of certain services, a statement of work (SOW) may be required either to initiate the process or as part of the agreement with the supplier or contractor. Capital expenditures have more stringent requirements, and approvals may involve consideration of the capital budgeting process.
Specification
Whenever a requisition is created, it’s important to include the necessary specifications to ensure that the correct material or service is being considered. As previously mentioned, a Statement of Work (SOW) may be required for certain services.
Specification – A clear, complete, and accurate statement of the technical requirements of a material, an item, or a service, and of the procedure to determine if the requirements are met.
When it comes to specifications, there are three main categories to consider: quantity, price, and function. Quantity and price requirements involve understanding the economies of scale and the economic value that the company is willing to pay. However, functional requirements are more complex and require greater attention. It is important to determine the specific function that a part is expected to perform, as it can greatly impact the price and quantity requirements.
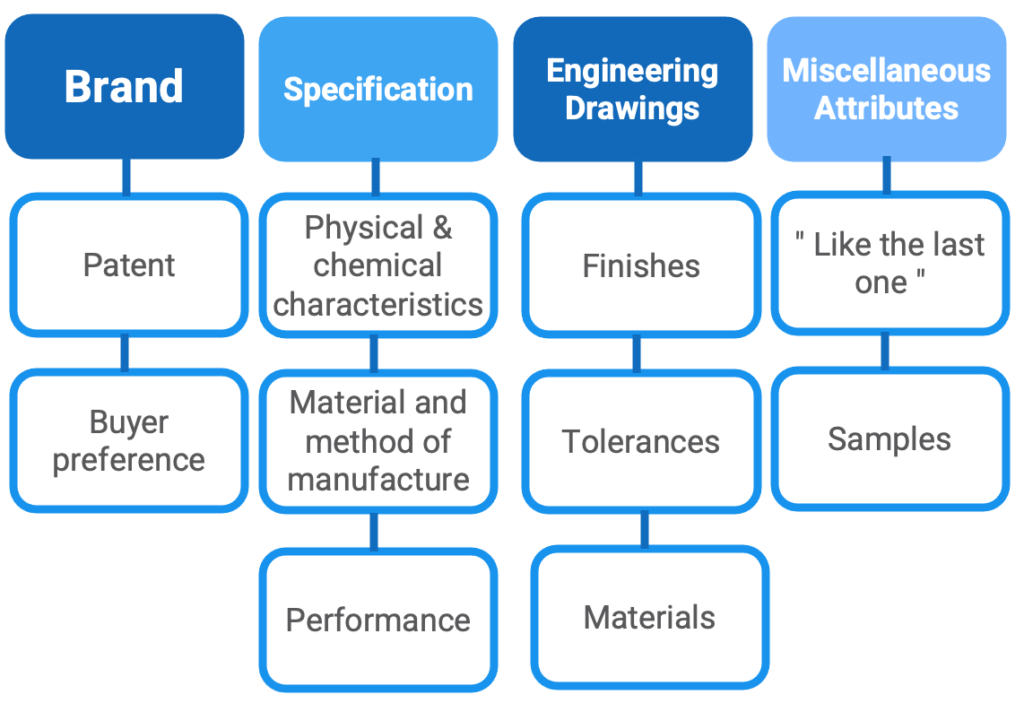
The functional specification can be categorized in four areas that include:
1. Brand
2. Specification of characteristics, material, performance or method of manufacture
3. Engineering drawings
4. Miscellaneous attributes
When companies engage in strategic procurement, they often utilize value analysis. This involves multi-disciplinary teams or other forms of collaboration during the design phase to assess features and potentially lower costs while ensuring optimal material functionality.
Value Analysis – The systematic use of techniques that identify a required function, establish a value for that function and finally provide that function as the lowest total cost.