As sustainability becomes more widespread, it can be challenging to align corporate and functional objectives. For instance, sustainable sourcing policies may result in higher sourcing costs, which could conflict with cost-control objectives. Therefore, selecting the most eco-friendly supplier may not guarantee the lowest total cost. Since procurement represents other functions in the organization, the entire team must be committed to the same sustainability agenda.
Below are some of the conflicts or trade-offs that may occur from sustainable procurement decisions:
1. Sourcing materials in “low-cost” countries to meet cost objectives may not fulfill CSR objectives or can increase the risk of the following: intellectual property loss, unstable economics, and a disruption in supply chain.
2. Applying diversity principles by selecting of minority-owned business may impact cost performance.
3. Sourcing from a wider spectrum to ensure supply sustainability may mean not using a favorite, well-known supplier.
4. Sourcing in lower-income countries with the objective of helping develop capacity within them must be weighed against legislative policies, communication and cultural issues; possibly different expectations of quality and performance standards must also be considered.
5. Sourcing with a company that uses unfair labor practices to get a lower price runs the risk of reputation damage, versus using potentially higher price companies that comply with ethical sourcing.
6. Using environmentally-friendly products and processes may impact quality or failure rates, leading to liability claims.
7. Measuring supplier performance against a new range of criteria may prevent some existing suppliers from being awarded contracts.
8. Incorporating sustainability requirements into specifications to achieve objectives may impact cost or appearance.
Challenges
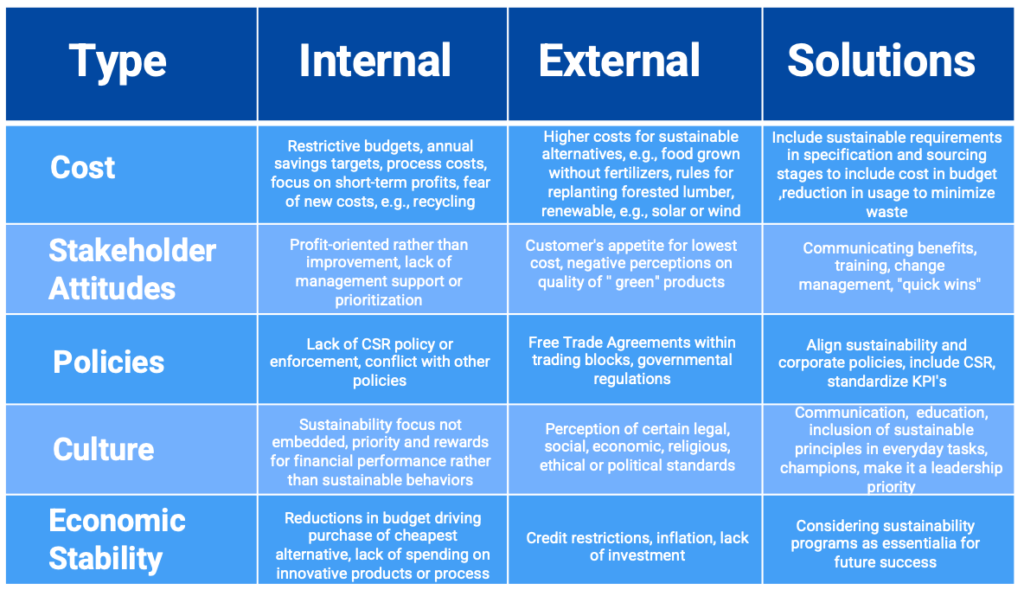
Apart from the trade-offs, there may be additional challenges or obstacles to achieving sustainability that may arise from both internal and external factors within an organization. The table below outlines some common barriers and suggests potential solutions to overcome them.