In simplest terms blockchain is a shared, unchangeable ledger of transactions. All transactions are considered “blocks,” which are joined together as the digital chain for that product, allowing for more transparency and visibility to the route the product took before reaching the marketplace. A blockchain is a form of technology that facilitates secure communication between partners.

Basic Principles of Blockchain Technology
Following are the basic principles of blockchain technology:
- It uses a distributed database, so that each participant in the blockchain has access to the transaction history. No single entity controls the information within the database.
- It is a private, secure, peer-to-peer network so that communication occurs directly between blockchain parties. Transactions are available to all member of a particular blockchain.
- Real-time transactions are entered into the database and are secure, irreversible and tamper-resistant. This provides for accuracy and integrity, as the data exists in a permanent transactional “chain.”
Watch the short video to review some of the key concepts to remember about blockchain.

Download video transcript here.
Uses of Blockchain within Procurement
Examples of uses of blockchain within procurement would be: tracking of purchases, change orders, change orders, and receipts; tracking the shipment of goods and documents from anywhere in the supply chain; and the ability to evaluate supplier risk based on how their materials are sourced.
The value and benefits that blockchain brings to the supply chain are:
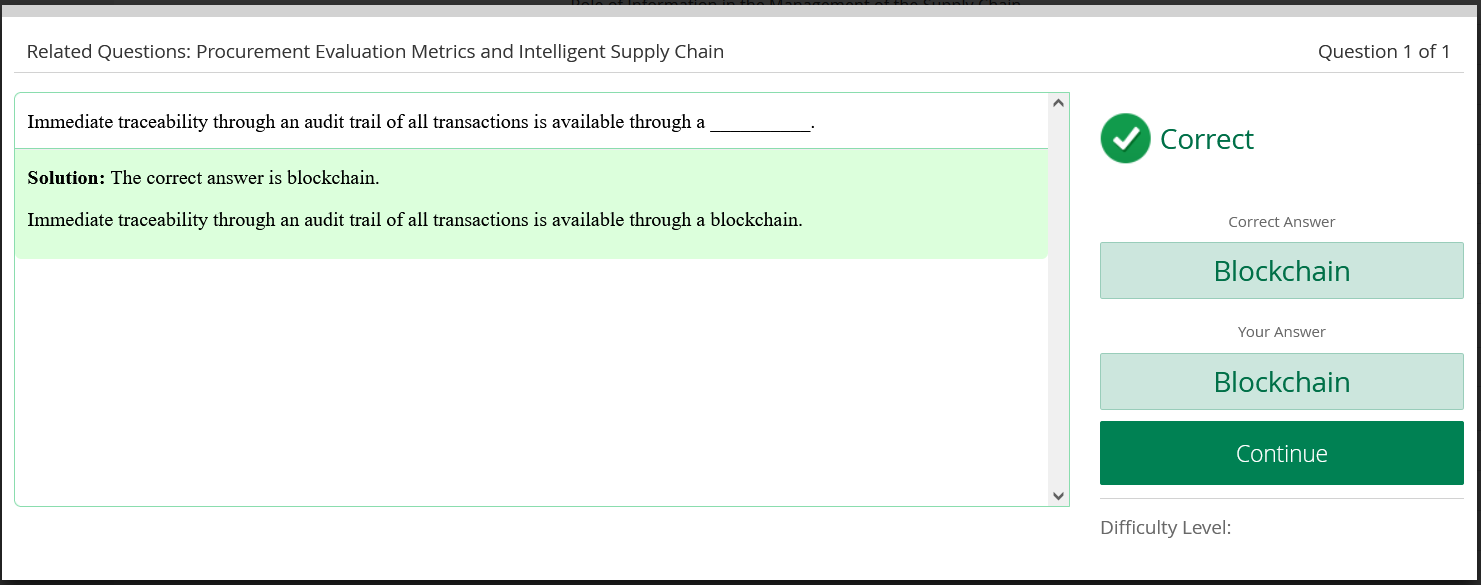
- Immediate traceability through a comprehensive audit trail covering all touchpoints from point of origin to final destination.
- Easier tracking of root causes of quality problems back through the supply chain where specifications are recorded
- Protection of data integrity, including the prevention of data breaches and counterfeiting, due to the increased security of the permanent transaction ledger
- Improved scalability from traditional databases, as it allows for any number of participants and unlimited touchpoints
Example
Watch the short video to learn more about how blockchain can be used in the food supply chain.

Download video transcript here.