Successful management of purchase orders requires the creation and continuous upkeep of crucial databases. Typically, multiple departments collaborate to create and maintain these databases, ensuring effective procurement management.
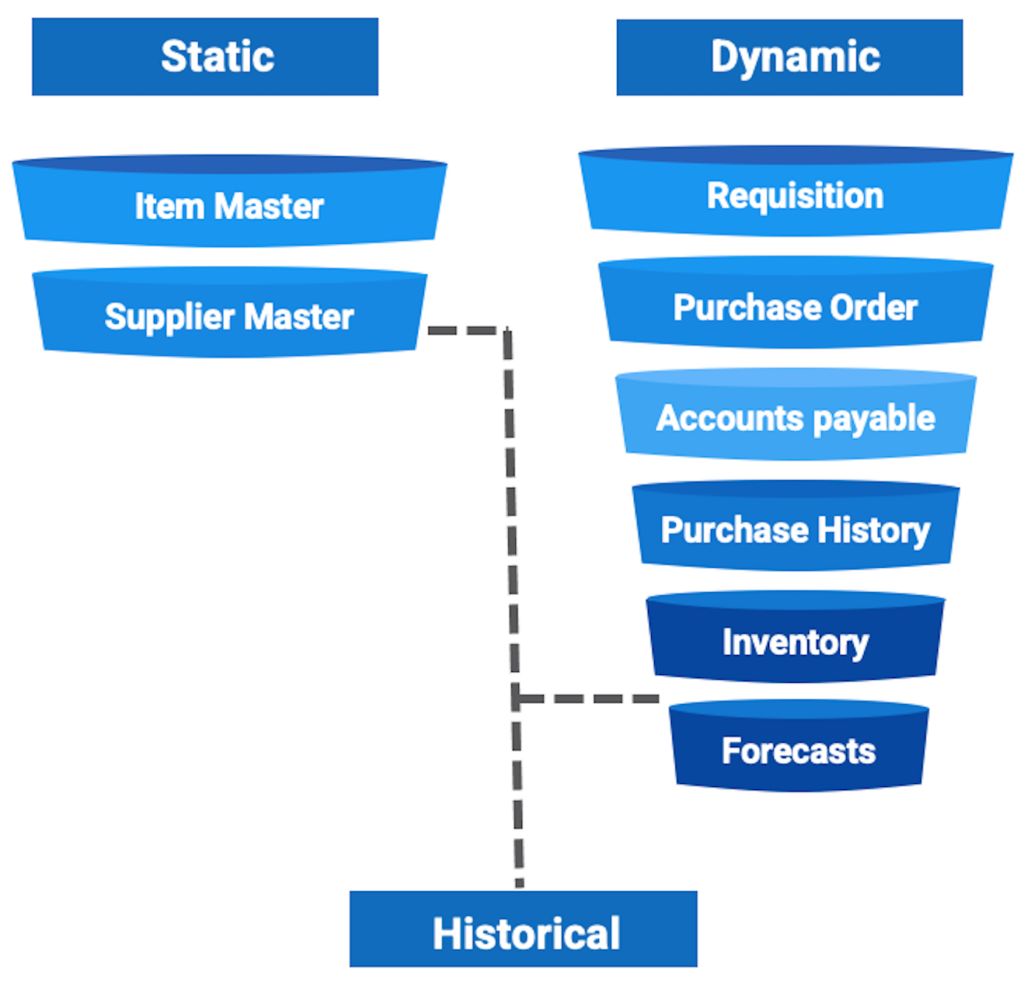
Static Purchasing Databases
The files within this category are considered static as they require deliberate creation or modification by a planner and are typically not impacted by purchase order processing. It is essential to establish these files prior to initiating any purchasing activity.
There are fundamental files in this grouping:
1. The item master is a comprehensive record containing item descriptions, classifications, costs, specifications, planning methods, lead times, order policies, and safety stock.
2. The supplier master contains key details such as the supplier name, status, and address. Additionally, it may include information about discounts, freight and delivery terms, currencies, payment terms, tolerances, and invoicing options for each supplier.
Dynamic Purchasing Databases
The files in this grouping are variable because they will change automatically whenever a purchase order is entered, changed, or transacted. These files provide the entire business with a window into order status and transaction history. Several files in this grouping include:
1. To source and purchase products and services, requisitions are necessary. The file provided contains both open and closed requisitions.
2. This file includes all open purchase orders and is used to review the status of POs.
3. Accounts payable is a record of the value of acquired products and services that a business owes to its suppliers. This file contains both open payables and payables history, created through ongoing purchase order receiving.
4. This database records all transactions, cancellations, and completions made to purchase orders, requisitions, receiving, request for proposals (RFPs), and more. It is essential for generating purchase performance and statistical reporting.
5. Item inventory counts are updated each time a transaction occurs, such as a receipt or when an item is removed from inventory for production. Before placing a new purchase order, inventory levels are checked.
6. Forecasts provide an estimate of future demand for products and services. Purchasing professionals can use forecasts to anticipate the materials needed to meet estimated demand.
Historical Databases
After transactions take place, they are recorded as transaction history and can be analyzed further. This history can include completed and cancelled purchase orders, requisitions, receipts (such as packing slips), request for proposals (RFPs), and other relevant data. It is crucial for generating purchase performance reports and statistical analysis.
Additionally, data can be stored in a data warehouse, a repository of information specifically designed to aid in making informed decisions. Data warehouses often combine data from various systems, which can then be accessed using specialized query tools.
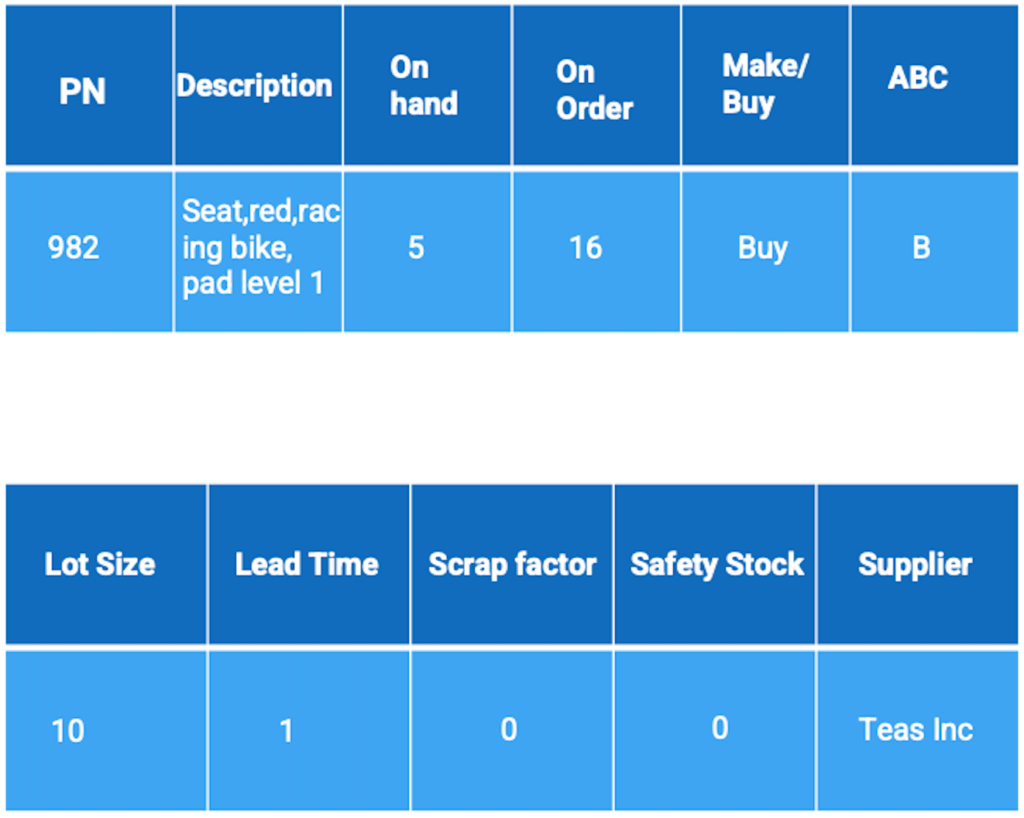
Item Master and Item Status
It is important to maintain accurate records for various items such as the item master and item status to ensure that the correct parts and quantities are available to meet demand.
Please refer to the provided image for an example.
There are currently 5 pieces of Part 982 available and 16 pieces on order from a supplier. This item is classified as a “buy” item from Taes Inc. and typically has a lead time of 1 week. Orders for this item are usually made in lots of 10, so it’s possible that a partial order has already been received with the 16 pieces on order. It’s important to ensure that this information is accurate to ensure efficient purchasing. Record accuracy is crucial in this process.